Case Study Test
A variety of topics were presented in the 1995 Case Study columns, including seven soft tissue lesions, one skin condition, two bone tumors, and one tooth abnormality. The following 44 questions will allow you to review the 11 columns and determine your diagnostic skills. After completing the Case Study test below, turn to page 39 to check your answers.
Joen Iannucci Haring, DDS, MS
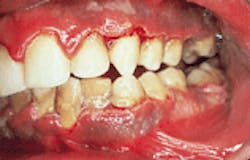
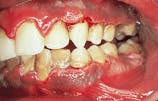
Case 1
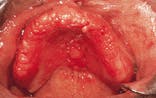
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG)
1. Identify the predisposing factor(s) for ANUG.
a. decreased resistance to infection
b. heavy smoking
c. poor oral hygiene
d. increased stress
e. all of the above
2. Identify the origin of ANUG.
a. viral
b. bacterial
c. fungal
d. parasitic
e. autoimmune
3. Identify which of the following is NOT a feature of ANUG.
a. tissue fibrosis
b. tissue sloughing
c. necrotic interdental papillae
d. erythematous gingiva
e. pain and bleeding
4. Identify the TRUE statement(s) concerning ANUG.
a. occurs in persons aged 15-35
b. occurs with fever and lymphadenopathy
c. affects mandibular anterior gingiva
d. characterized by a rapid onset
e. all of the above
Case 2
Osteoma
1. Identify the most common location for the osteoma.
a. anterior mandible
b. angle of the mandible
c. anterior maxilla
d. posterior maxilla
e. none of the above
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of the osteoma.
a. radiolucent
b. radiopaque
c. mixed lucent/opaque
d. radiolucent or radiopaque
e. none of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for the osteoma.
a. none
b. cryosurgery
c. surgical excision
d. electrosurgery
e. radiation therapy
4. Identify the TRUE statement concerning the osteoma.
a. often occurs in children
b. often occurs in multiples
c. often involves the maxilla
d. often asymptomatic
e. often fast-growing
Case 3
Lymphangioma
1. Identify the tissue of origin for the lymphangioma.
a. lymphatic vessels
b. blood vessels
c. glandular tissue
d. nerve tissue
e. none of the above
2. Identify the best method to diagnose the lymphangioma.
a. clinical appearance
b. histologic examination
c. cytologic examination
d. culture techniques
e. none of the above
3. Identify the TRUE statement(s) concerning the lymphangioma.
a. occurs as a soft mass
b. occurs on the tongue and palate
c. classified as a congenital lesion
d. painless when compressed
e. all of the above
4. Identify the treatment of choice for the lymphangioma.
a. none
b. surgical removal
c. cryosurgery
d. corticosteroid medication
e. anti-inflammatory medication
Case 4
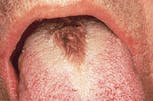
Hairy tongue
1. Identify the predisposing factor(s) for hairy tongue.
a. heavy smoking
b. poor oral hygiene
c. candidiasis
d. antibiotic use
e. all of the above
2. Identify the most common location for hairy tongue.
a. posterior dorsal tongue
b. anterior dorsal tongue
c. anterior ventral tongue
d. lateral borders of tongue
e. any of the above
3. Identify the TRUE statement concerning hairy tongue.
a. elongation of fungiform papillae occurs
b. may appear white, brown or black
c. a biopsy is required for diagnosis
d. also known as hairy leukoplakia
e. none of the above
4. Identify the treatment of choice for hairy tongue.
a. surgical excision
b. improved oral hygiene
c. antibiotic medication
d. anti-inflammatory medication
e. corticosteroid medication
Case 5
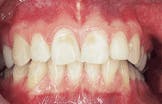
Erosion
1. Identify the cause of erosion.
a. bacteria
b. abnormal mechanical forces
c. functional wear
d. acids
e. none of the above
2. Identify the areas likely to exhibit erosion with a lemon-sucking habit.
a. facial surfaces of anterior teeth
b. lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
c. interproximal surfaces of anterior teeth
d. any of the above
e. none of the above
3. Identify the areas likely to exhibit erosion with chronic vomiting.
a. facial surfaces of anterior teeth
b. lingual surfaces of anterior teeth
c. interproximal surfaces of anterior teeth
d. any of the above
e. none of the above
4. Identify the TRUE statement concerning erosion.
a. resembles attrition
b. resembles caries
c. always asymptomatic
d. treated with restorative procedures
e. none of the above
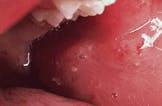
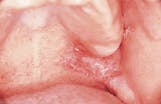
Case 6
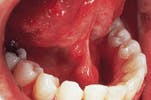
Lymphoepithelial cyst
1. Identify the most common location for the lymphoepithelial cyst.
a. hard palate
b. soft palate
c. floor of mouth
d. buccal mucosa
e. none of the above
2. Identify the TRUE statement concerning the lymphoepithelial cyst.
a. occurs in older adults
b. often appears ulcerated
c. painful when compressed
d appears pink or yellow
e. none of the above
3. Identify the lesion that is unlikely to be confused with the lymphoepithelial cyst.
a. pleomorphic adenoma
b. lipoma
c. mucocele
d. sialolith
e. giant cell fibroma
4. Identify the treatment of choice for the lymphoepithelial cyst.
a. cryosurgery
b. radiation therapy
c. surgical excision
d. antibiotic medication
e. any of the above
Case 7
Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia
1. Identify the TRUE statement(s) concerning IPH.
a. classified as a reactive condition
b. associated with poor denture hygiene
c. associated with ill-fitting dentures
d. may occur in persons without dentures
e. all of the above
2. Identify the FALSE statement(s) concerning IPH.
a. caused by Candida albicans
b. often occurs in mucobuccal fold
c. appears white or grayish-white
d. seen in 35% of denture wearers
e. all of the above
3. Identify the most common method to diagnose IPH.
a. clinical appearance
b. histologic examination
c. cytologic examination
d. culture techniques
e. none of the above
4. Identify the treatment of choice for IPH.
a. curettage
b. surgical excision
c. electrosurgery
d. cryosurgery
e. any of the above
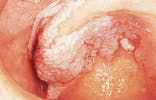
Case 8
Verrucous carcinoma
1. Identify the most important etiologic factor linked to verrucous carcinoma.
a. sun exposure
b. alcohol consumption
c. pipe smoking
d. smokeless tobacco products
e. none of the above
2. Identify the TRUE statement concerning verrucous carcinoma.
a. comprises 20% of all oral cancers
b. exhibits a warty surface texture
c. occurs on the tongue and lip
d. metastasis occurs early
e. painful when compressed
3. Identify the treatment of choice for verrucous carcinoma.
a. none
b. cryosurgery
c. surgical excision
d. chemotherapy
e. radiation therapy
4. Identify the FALSE statement concerning verrucous carcinoma.
a. occurs only in males
b. occurs in older adults
c. asymptomatic and slow growing
d. resembles a "frozen doormat"
e. usually appears white
Case 9
Pemphigus vulgaris
1. Identify the origin of pemphigus vulgaris.
a. viral
b. bacterial
c. fungal
d. neoplastic
e. autoimmune
2. Identify the FALSE statement concerning pemphigus vulgaris.
a. oral lesions may occur without skin lesions
b. bullae are often seen intraorally
c. oral lesions cause severe pain
d. positive Nikolsky`s sign is seen on the skin
e. diagnosis is confirmed with immunofluorescence studies
3. Identify the TRUE statement concerning pemphigus vulgaris.
a. affects skin and oral cavity
b. lesions include bullae and ulcerations
c. occurs in persons aged 30-50
d. may result in death
e. all of the above
4. Identify the treatment of choice for pemphigus vulgaris.
a. surgery
b. radiation therapy
c. chemotherapy
d. immunosuppressive therapy
e. none of the above
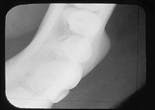
Case 10
Complex odontoma
1. Identify the most common location for the complex odontoma.
a. anterior mandible
b. posterior mandible
c. anterior maxilla
d. posterior maxilla
e. posterior maxilla or mandible
2. Identify the radiographic appearance of the complex odontoma.
a. multilocular radiolucency
b. unilocular radiolucency
c. radiopacity with radiolucent rim
d. radiolucency with radiopaque flecks
e. none of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for the complex odontoma.
a. none
b. cryosurgery
c. surgical excision
d. electrosurgery
e. radiation therapy
4. Identify the TRUE statement concerning the complex odontoma.
a. often occurs in adults
b. characterized by tooth-like structures
c. characterized by a mass of amorphous hard tissue
d. diagnosis based on radiographic appearance
e. often symptomatic
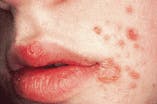
Case 11
Impetigo
1. Identify the origin of impetigo.
a. viral
b. bacterial
c. fungal
d. parasitic
e. autoimmune
2. Identify the major predisposing factor for impetigo.
a. decreased resistance to infection
b. poor oral hygiene
c. non-intact skin
d. increased stress
e. none of the above
3. Identify the treatment of choice for impetigo.
a. none
b. topical antifungal medication
c. topical antibiotic medication
d. topical anti-inflammatory medication
e. topical corticosteroid medication
4. Identify the TRUE statement concerning impetigo.
a. often occurs in adults
b. often asymptomatic
c. affects skin and oral cavity
d. appears as honey-colored crusts
e. caused by Candida albicans
Case Study Test Answers
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
v
CASE 1: 1 = e; 2 = b; 3 = a; 4 = e
CASE 2: 1 = b; 2 = b; 3 = c; 4 = d
CASE 3: 1 = a; 2 = b; 3 = e; 4 = b
CASE 4: 1 = e; 2 = a; 3 = b; 4 = b
CASE 5: 1 = d; 2 = a; 3 = b; 4 = d
CASE 6: 1 = c; 2 = d; 3 = e; 4 = c
CASE 7: 1 = e; 2 = e; 3 = a; 4 = e
CASE 8: 1 = d; 2 = b; 3 = c; 4 = a
CASE 9: 1 = e; 2 = b; 3 = e; 4 = d
CASE 10: 1 = e; 2 = c; 3 = c; 4 = c
CASE 11: 1 = b; 2 = c; 3 = c; 4 = d
Joen Iannucci Haring, DDS, MS, is an associate professor of clinical dentistry, Section of Diagnostic Services, The Ohio State University College of Dentistry.