Case Study Test
By Joen Iannucci Haring
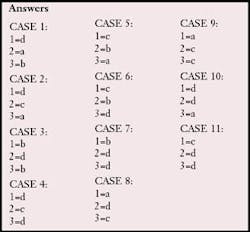
A variety of topics were presented in the 2003 Case Study columns. Use the following 33 questions to review and test your knowledge concerning this year's eleven columns. After completing the Case Study Test, turn to page 52 to check your answers.
CASE 1
Lateral periodontal cyst (LPC)
1. Where is the LPC likely to occur?
a. mandibular canine area
b. mandibular incisor area
c. mandibular premolar area
d. all of the above
2. What is the radiographic appearance of the LPC?
a. round/ovoid radiolucency, well-defined borders
b. round/ovoid radiolucency, ill-defined borders
c. round/ovoid radiopacity, well-defined borders
d. round/ovoid radiopacity, ill-defined borders
3. What is the preferred treatment for the LPC?
a. no treatment is necessary
b. surgical removal
c. laser surgery
d. none of the above
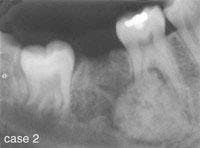
CASE 2
Cementoblastoma
1. What is the likely age group for persons with a cementoblastoma?a. 40 - 50b. 50 - 60c. 60 - 702. Where is the cementoblastoma likely to occur?
a. posterior maxilla
b. anterior maxilla
c. posterior mandible
d. anterior mandible
3. What is the radiographic appearance of the cementoblastoma?
a. radiopaque mass with radiolucent rim
b. multilocular radiolucency
c. mixed lucent-opaque lesion
d. none of the above
CASE 3
Ranula
1. Where is the ranula likely to occur?
a. lips
b. floor of mouth
c. labial mucosa
d. hard palate
2. What salivary gland(s) are involved in the formation of the ranula?
a. sublingual gland
b. submandibular gland
c. minor salivary glands
d. any of the above
3. What is the preferred treatment for the ranula?
a. no treatment required
b. marsupialization
c. radiation therapy
d. none of the above
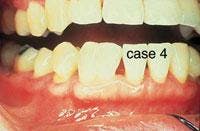
CASE 4
Fusion
1. What causes fusion?
a. tetracycline use
b. crowding
c. trauma
d. both b & c
2. Identify the true statement concerning fusion.
a. permanent dentition affected most often
b. results in an increased number of teeth
c. anterior teeth affected most often
d. premolars affected most often
3. Identify the true statement(s) concerning the appearance of fusion.
a. one large crown with observable separation
b. size may range from normal to twice normal
c. clinically resembles a geminated tooth
d. all of the above
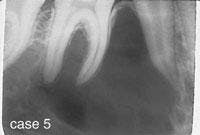
CASE 5
Traumatic bone cyst (TBC)
1. Where is the TBC likely to occur?
a. long bones
b. mandible
c. both a & b
d. none of the above
2. What is the likely age group for persons with a TBC?
a. < 10
b. 10 - 20
c. 20 - 30
d. > 30
3. What is the radiographic appearance of the TBC?
a. radiolucent
c. mixed lucent/opaque
b. radiopaque
d. any of the above
CASE 6
Peripheral giant cell granuloma (PGCG)
1. What causes a PGCG?
a. irritation
b. injury
c. both a & b
d. none of the above
2. Where is the PGCG likely to occur?
a. hard palate
b. gingiva
c. floor of mouth
d. any of the above
3. What is the preferred treatment for the PGCG?
a. surgical excision
b. removal of irritation sources (calculus)
c. no treatment necessary
d. both a & b
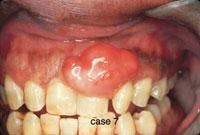
CASE 7
Peripheral ossifying fibroma (POF)
1. Where is the POF likely to occur?
a. hard palate
b. gingiva
c. floor of mouth
d. any of the above
2. What is the appearance of the POF?
a. pale pink or reddish color
b. sessile or pedunculated
c. smooth surface
d. any of the above
3. What lesion may be confused with the POF?
a. pyogenic granuloma
b. peripheral giant cell granuloma
c. irritation fibroma
d. any of the above
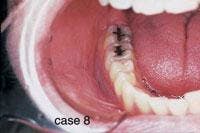
CASE 8
Smokeless tobacco keratosis
1. Where is the smokeless tobacco keratosis likely to occur?
a. mucobuccal fold area
b. dorsal tongue
c. hard palate
d. gingiva
2. What is the clinical appearance of the smokeless tobacco keratosis?
a. white color
b. raised or flat contours
c. smooth, granular or corrugated
d. any of the above
3. What is the recommended treatment for the smokeless tobacco keratosis?
a. surgical removal
b. radiation therapy
c. discontinue use of product
d. none of the above
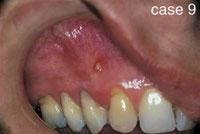
CASE 9
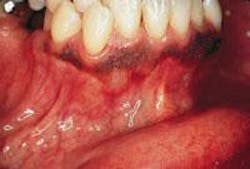
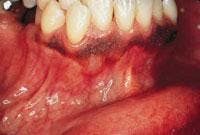
Parulis
1. What is a common term used for the parulis?
a. gum boil
b. fistula
c. draining fistula
d. any of the above
2. Where is a parulis associated with a non-vital tooth likely to occur?
a. apical to the tooth>
b. near the mucogingival junction
c. both a & b
d. none of the above
3. What is the recommended treatment for a parulis?
a. root canal of the affected tooth
b. extraction of the affected tooth
c. either a or b
d. no treatment necessary
CASE 10
Amalgam tattoo
1. What is the appearance of the amalgam tattoo?
a. blue, black or gray color
b. diffuse border
c. flat
d. any of the above
2. How is the amalgam tattoo most often diagnosed?
a. clinical features
b. histologic features
c. radiographic appearance
d. both a & c
3. What is the recommended treatment for the amalgam tattoo?
a. no treatment necessary
b. surgical removal
c. radiation therapy
d. any of the above
CASE 11
Vascular malformation
1. Where is the vascular malformation likely to occur?
a. trunk
b. limbs
c. head and neck
d. all of the above
2. How is the vascular malformation diagnosed?
a. duration history
b. clinical features
c. blanches with pressure
d. all of the above
3. What is the treatment for the vascular malformation?
a. no treatment may be required
b. surgical removal
c. sclerotherapy
d. any of the above
Joen Iannucci Haring, DDS, MS, is a professor of clinical dentistry, Section of Primary Care, The Ohio State University College of Dentistry.