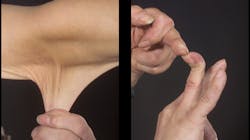
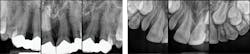
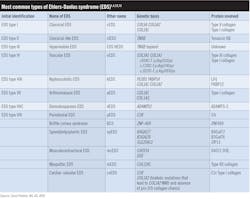
Recognizing the clinical signs of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Collagen exists in many different forms, and each has a unique function within our bodies. For example, collagen type I forms the scaffolds for mineralized tissues and is the major component in all connective tissue. A good example would be the periodontal ligament (PDL) that is comprised of collagen type I (80%) and type III (20%), with lesser amounts of several other types of collagen.3 When there is disruption in collagen formation or when it is poorly synthesized, the bones, teeth, and various structures are weakened and the structural foundation is impaired.
EDS type VIII is associated with periodontal disease/variable connective tissue features and is designated a periodontitis form.4 This form is characteristic of tooth loss, periodontal disease, and periodontal ligament destruction along with alveolar bone destruction. Tooth loss may occur in the early teen years of patients who have this type of EDS.5
Specifically, EDS results because of genetic defects on chromosomes 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 9, 12q, 13, and 17. Any one of the genes can cause varying degrees of defective collagen. The Ehlers-Danlos Society also has a genetic classification structure of EDS, listing groups according to similarities in the way the responsible genes affect the body.1,3,4
Studies show that pain is felt in the peripheral neurons in mice and has been noted as a genetic mutation in the matrix protein layer. Consequently, local anesthesia is a case-by-case decision. One theory as to why anesthesia is less effective in some patients is that the connective tissue is broken down and has a looseness that acts as a barrier.8-10
As always, continue to ask good questions and always listen to your patients.
- EDS Types. The Ehlers-Danlos Society. https://www.ehlers-danlos.com/eds-types/
- Delong L, Burkhart NW. General and Oral Pathology for the Dental Hygienist. Enhanced 3rd ed. Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019.
- Kaur P, Kakar V. Collagen: role in oral tissues: a review. Int J Sci Res. 2014;3(5):273-276. https://www.ijsr.net/archive/v3i5/MDIwMTMxNjg2.pdf
- Ehlers-Danlos syndromes. The Medical Biochemistry Page. https://themedicalbiochemistrypage.org/ehlers-danlos-syndromes/
- Reinstein E, DeLozier CD, Simon Z, Bannykh S, Rimoin DL, Curry CJ. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIII is clinically heterogeneous disorder associated primarily with periodontal disease, and variable connective tissue features. Eur J Hum Genet. 2013;21(2):233-236. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2012.132
- Whitaker JK, Alexander P, Chau DYS, Tint NL. Severe conjunctivochalasis in association with classic type Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. BMC Ophthalmol. 2012;12:47. doi:10.1186/1471-2415-12-47
- Premalatha S, Sarveswari KN, Lahiri K. Reverse-namaskar: a new sign in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome: a family pedigree study of four generations. Indian J Dermatol. 2010;55(1):86-91. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.60360
- Schubart JR, Schaefer E, Janicki P, et al. Resistance to local anesthesia in people with the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes presenting for dental surgery. J Dent Anesth Pain Med. 2019;19(5):261-270. doi:10.17245/jdapm.2019.19.5.261
- Wiesmann T, Castori M, Malfait F, Wulf H. Recommendations for anesthesia and perioperative management in patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome(s). Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2014;9:109. doi:10.1186/s13023-014-0109-5
- Calcaterra N. Dental local anesthesia and Ehlers Danlos Syndrome. Directions in Dentistry. April 24, 2016. http://directionsindentistry.net/dental-local-anesthesia-ehler-danlos-syndrome/
- Glick M. Burket’s Oral Medicine. 12th ed. People’s Medical Publishing House; 2015.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, Neuhaus IM. Andrews’ Diseases of the Skin. Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Elsevier; 2016:502-505.
- Younger DS. The Autoimmune Brain. A Five-Step Plan for Treating Chronic Pain, Depression, Anxiety, Fatigue, and Attention Disorders. Rowman & Littlefield; 2019:47, 205, 223.
Nancy W. Burkhart, EdD, MEd, BS, RDH, AAFAAOM, is an adjunct professor in the department of periodontics-stomatology at Texas A&M University College of Dentistry. Dr. Burkhart is founder and cohost of the International Oral Lichen Planus Support Group (dentistry.tamhsc.edu/olp) and coauthor of General and Oral Pathology for the Dental Hygienist, in its third edition. She was awarded an affiliate fellow status in the American Academy of Oral Medicine in 2016. She received the Dental Professional of the Year award in 2017 through the International Pemphigus and Pemphigoid Foundation and is a 2017 Sunstar/Award of Distinction recipient. She can be contacted at [email protected].
Carol Perkins, BA, AS, RDH, has worked as a dental hygienist for 45 years in private practice in California. She was presented the Leadership & Professionalism Award by the Fresno Madera Dental Society at her dental hygiene graduation ceremony in 1975 at Fresno City College. She has been published in Access Magazine by the American Dental Hygiene Association and has contributed to RDH magazine. She frequently does outreach to children by teaching hygiene in grammar and special needs schools. Contact her at [email protected].
About the Author
Nancy W. Burkhart, EdD, MEd, BSDH, AAFAAOM
NANCY W. BURKHART, EdD, MEd, BSDH, AAFAAOM, is an adjunct professor in the Department of Periodontics-Stomatology, College of Dentistry, Texas A&M University, Dallas, Texas. She is founder and cohost of the International Oral Lichen Planus Support Group (dentistry.tamhsc.edu/olp/) and coauthor of General and Oral Pathology for the Dental Hygienist, now in its third edition. Dr. Burkhart is an academic affiliate fellow with the American Academy of Oral Medicine, where she also serves as chair of the Affiliate Fellowship Program Committee. She was awarded the Dental Professional of the Year in 2017 through the International Pemphigus and Pemphigoid Foundation, and she is a 2017 Sunstar/RDH Award of Distinction recipient. Her professional interests are in the areas of oral medicine and the relationship between oral and whole-body health, with a focus on mucosal disease and early oral cancer detection. Contact her at [email protected].

Carol Perkins, BA, AS, RDH
Carol Perkins, BA, AS, RDH, has worked as a dental hygienist for 44 years in private practice in California. She was presented the Leadership & Professionalism Award by the Fresno Madera Dental Society at her dental hygiene graduation ceremony in 1975 at Fresno City College. She has been published in Access Magazine by the American Dental Hygiene Association and has contributed to RDH magazine. She frequently does outreach to children by teaching hygiene in grammar and special needs schools. Contact her at [email protected].
Updated February 1, 2020