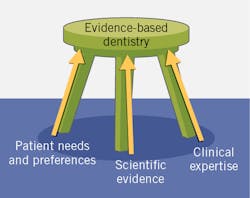
Evidence-based care is a key component in the delivery of care in medicine and dentistry. First developed as evidence-based practice (EBP) in medicine,1 it was then introduced into other disciplines, including as evidence-based dentistry (EBD). This is defined by the American Dental Association as “an approach to oral health care that requires the judicious integration of systematic assessments of clinically relevant scientific evidence, relating to the patient’s oral and medical condition and history, with the dentist’s clinical expertise and the patient’s treatment needs and preferences.”2 The American Dental Hygienists’ Association advocates “evidence-based, patient/client-centered dental hygiene practice.”3
In EBD, the balance in which criteria take precedence depends upon what relevant evidence is available as well as the relative relevance of the other criteria. However, if patients do not want or will not accept a treatment, it does not matter how robust the relevant scientific evidence is.
Evidence levels and challenges
Insufficient information about a protocol or therapy’s overall efficacy is considered a lack of evidence. Reasons for a lack of evidence include an absence or paucity of studies due to extensive resource requirements, poor-quality studies, ethics precluding use of a placebo, or due to prior real or perceived lack of need to study a potential use of a particular therapy or agent. Knowledge is recognized as a “moving target.”5 Unanticipated and unprecedented changes can also be disruptive and create a knowledge gap, as is the case during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Biologic plausibility
In dentistry, biologic plausibility is applicable to prerinsing with 1.5% hydrogen peroxide or 0.2% povidone-iodine, as SARS-CoV-2 is susceptible to oxidation, a potential mechanism to reduce viral loads in treatment-generated aerosols.11 Biologic plausibility and precedence is also applied to ideation and current research on vaccines such as those targeting the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein that fuses to ACE2 human receptors, while clinical trials currently underway will provide evidence on safety and efficacy (figure 3).12
Changes in protocols for patient care
Recommendations and protocols have also been modified due to COVID-19. For head and neck cancers, availability of personal protective equipment influences treatment choices.13 In dentistry, recommended changes include the use of manual scalers along with a recommendation against performing ultrasonic scaling.14 The provision of alternative treatments that generate less or no aerosol, use of alternative materials, and less invasive treatments have also been recommended in dentistry. Guidelines during COVID-19 differ by organization and by country, which can cause confusion.
Conclusions
EBD distills the best available scientific evidence and patient and clinician factors, promoting optimized and personalized care. It is also true that dentistry and medicine are facing unanticipated challenges due to the COVID-19 pandemic as well as knowledge gaps. Building knowledge through research is essential, and EBP and EBD remain central to patient care.
Editor’s note: This article is sponsored by Colgate and has been reviewed for editorial integrity. For more information on our editorial standards, see rdhmag.com/page/submission-guidelines.
References
- Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JA, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t. BMJ. 1996;312(7023):71-72. doi:10.1136/bmj.312.7023.71
- Policy on evidence-based dentistry. American Dental Association. Updated August 29, 2013. http://www.ada.org/en/about-the-ada/ada-positions-policies-and-statements/policy-on-evidence-based-dentistry
- ADHA Policy Manual. American Dental Hygienists’ Association. Adopted June 2019. https://www.adha.org/resources-docs/7614_Policy_Manual.pdf
- Clinical practice guidelines. American Dental Association. https://ebd.ada.org/en/evidence/guidelines
- Farley AJ, Feaster D, Schapmire TJ, et al. The challenges of implementing evidence based practice: Ethical considerations in practice, education, policy, and research. Soc Work Soc. 2009;7(2):246-259.
- Hill AB. The environment and disease: association or causation? 1965. J R Soc Med. 2015;108(1):32-37. doi:10.1177/0141076814562718
- Dailey J, Rosman L, Silbergeld EK. Evaluating biological plausibility in supporting evidence for action through systematic reviews in public health. Public Health. 2018;165:48-57. doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2018.08.015
- Duan K, Liu B, Li C, et al. Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(17):9490-9496. doi:10.1073/pnas.2004168117
- Rothan HA, Byrareddy SN. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. J Autoimmun. 2020;109:102433. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
- Joyner MJ, Wright RS, Fairweather D, et al. Early safety indicators of COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 5,000 patients. J Clin Invest. 2020;140200. doi:10.1172/JCI140200
- Peng X, Xu X, Li Y, Cheng L, Zhou X, Ren B. Transmission routes of 2019-nCoV and controls in dental practice. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):9. doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0075-9
- Amanat F, Krammer F. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Status Report. Immunity. 2020;52(4):583-589. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.007
- Day AT, Sher DJ, Lee RC, et al. Head and neck oncology during the COVID-19 pandemic: Reconsidering traditional treatment paradigms in light of new surgical and other multilevel risks. Oral Oncol. 2020;105:104684. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104684
- Guidance for dental settings: Interim infection prevention and control guidance for dental settings during the COVID-19 response. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated June 17, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/dental-settings.html#Background
About the Author

Fiona M. Collins, BDS, MBA, MA
Fiona M. Collins, BDS, MBA, MA, is a national and international speaker and author, and has presented on infection control, the prevention and management of oral disease, pain, vaping, tobacco cessation, and materials. She is a member of the ADA, CDS, and OSAP; the ADA representative to the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI); a participant in standards working groups; and a fellow of the Pierre Fauchard Academy. Dr. Collins graduated as a general dentist from the University of Glasgow in Scotland and holds an MBA and an MA from Boston University.